Tkinter
- Create a program that draws the No Entry traffic sign, as shown in the image:
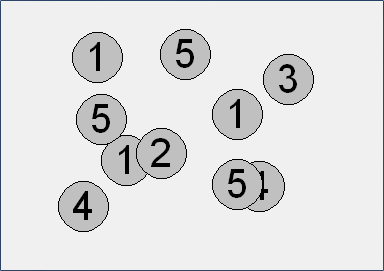
- Create a program mince.py and in it a function mince. The function should generate a random position and coin value from 1 to 5. The resulting image should look similar to the given example.
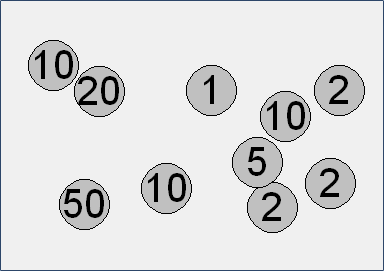
Call the function mince 10 times using a loop. 3. Modify the previous program so that only coins with values 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50 are generated.
When generating the coin values, use the command:
random.choice([1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50])
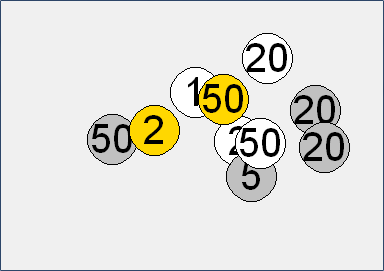
- The random.choice command can also be used to select colors. Modify the previous program so that the variable farba (color) is assigned using:
random.choice([‘silver’, ‘gold’, ‘white’])
and use this variable in the drawing command fill=farba.
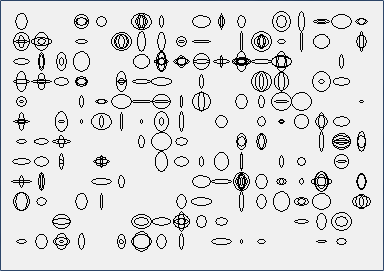
- Aliens have sent us the following message.
Try to reply with a similar message. Write a program called ufo_sprava.py that randomly generates such a message according to the following rules:
- Each message consists of 256 small ellipses.
- The ellipses are arranged in a grid with 18 columns and 12 rows.
- Each cell of the grid is 20x20 pixels.
Slovník - dictionary
Methods
Method Description
dict.keys() returns all keys
dict.values() returns all values
dict.items() returns all keys and values
dict.get(key) safe access to values
dict.pop(key) removes and returns value
-
Create a dictionary student with the following data:
"name": "Peter" "age": 21 "study_program": "Computer Science"
Print all keys and values.
-
Add a new key year with the value 2 to the existing dictionary student, and change age to 22.
-
For the given dictionary:
employee = { "name": "Jana", "position": "accountant", "salary": 1300 }
Print each key and its value in the format:
name: Jana
position: accountant
salary: 1300
-
From the dictionary products = {“apple”: 0.5, “pear”: 0.7, “banana”: 0.5} remove all items with the value 0.5.
-
For the dictionary countries = {“Slovakia”: “Bratislava”, “Czech Republic”: “Prague”} create a new one where the keys become values and values become keys.
-
You have two dictionaries:
daily_sales1 = {"apple": 3, "pear": 2} daily_sales2 = {"apple": 4, "banana": 5}
Create a single dictionary that contains all items. If keys repeat, sum their values. The output should look like this:
{"apple": 7, "pear": 2, "banana": 5}
-
Create a function word_count_dict(sentence) that returns a dictionary where the keys are words and the values are the number of their occurrences in the sentence. Example:
word_count_dict("dog meow dog meow meow")
Output:
{'dog': 2, 'meow': 3}